Table of Contents
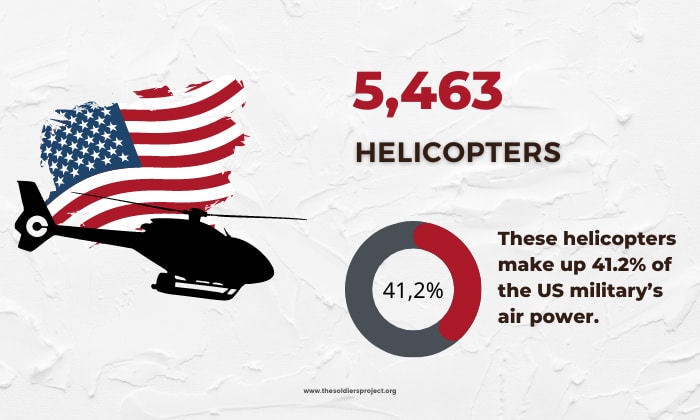
How many helicopters does the US Military have? According to Global Fire Power 2022, the US has 5,463 helicopters. These helicopters make up 41.2% of the US military’s air power.
Aside from this single number, though, it is worth learning about the types of helicopters in the military US and the military helicopter names. We have all that information below. So, read until the end!
US Military Helicopters
Compared to Other Countries
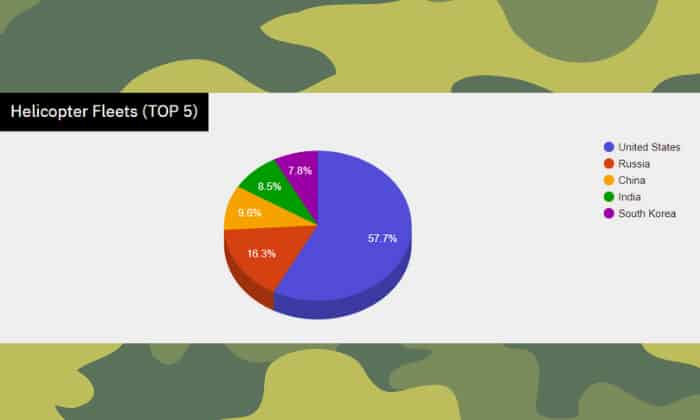
The US Army helicopter fleet is among the top 5, with 5,463 in total. The country with the second-largest fleet is Russia, with only 1,543 helicopters. China, coming in third, has only 912 helicopters. India (fourth) has 805 helicopters, and South Korea (fifth) has 739 helicopters.
Some countries have no helicopters, making up their military strength, at all. For example:
These countries operate only 1 helicopter:
Current US military helicopters are classified into seven types — trainer helicopters, utility helicopters, search and rescue helicopters, observation helicopters, maritime helicopters, transport helicopters, and attack helicopters.
Note: They are typically referred to as Army aviation helicopters but are the same across other service branches.
To help you understand these seven types of helicopters, we will provide an example of each and pictures! Read on!
Type 1: Trainer Helicopters
These helicopters are used for pilots in training. Usually, they are unarmored and do not carry weapons. An example of this type of helicopter is the Bell TH-57 Sea Ranger.
It is the military-converted Bell 206 helicopter. At present, it serves the US Marine Corps and Navy as a multi-purpose helicopter with two blades. The Bell TH-57 Sea Ranger entered service in 1968.
Its specifications are as follows:
It is mostly made of aluminum honeycomb. Outside, it is protected with aluminum skin and fiberglass. Its tubes are made of aluminum alloy, and it has an arched tail.
Its engine is the turboshaft Allison 250C20BJ with 1-stage centrifugal compressors, 6-stage axial, 2-stage axial power turbine, and 2-stage axial output turbine. The max thrust rate is 420 shaft horsepower.
Type 2: Utility Helicopter
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a well-known utility helicopter manufactured in 1979. You may have seen it in the 2001 Oscar-winning Ridley Scott film “Black Hawk Down.” It is an effective and fast-moving transport that can accommodate up to 11 members. Powered by twin GE-700 engines, it can move at 182 mph. Despite being a utility helicopter, it is equipped with machine guns.
Its specifications are as follows:
Apart from the US, the Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is also used by the Columbian, Japanese, and Korean forces. Since its debut, about 4,000 of it has been built.
Type 3: Search and Rescue Helicopters
An example of a search and rescue helicopter is the Sikorsky HH-60G Pave Hawk.
It is based on the US Army’s helicopter Black Hawk, but has its own upgraded systems, such as:
These help it locate survivors’ locations and perform rescue missions more efficiently.
Powered by two engines, the Pave Hawk can produce between 1,560 and 1,940 shaft horsepower in each. It has a four-blade rotor and four-blade tail rotor. It can fly up to 184 miles an hour and its service ceiling is 14,000 feet.
4 crew can be accommodated and there is room for other equipment as well as armaments. For example, there can be machine guns (7.62 mm or 12.7mm).
Since it entered service in 1991, it is used primarily by the US Air Force, in Panama, Desert Storm, Africa, the Middle East, Gulf regions, etc. Currently, it is also seeing action in Afghanistan and Iraq.
Type 4: Observation Helicopters
The Bell H-13 Sioux is a basic observation helicopter with a single engine. It was developed from the Bell 47, which was originally ordered by the British Army. When procured by the US military, it was operated by the Navy and Coast Guard. Later, in the Korean War and early in the Vietnam War, it was used by the Army.
It has three seats, a soap bubble canopy, exposed tail boom, and skid landing gear. It was typically armed with evacuation panniers and acrylic glass shields as well. In addition, it was fitted with a single engine, two external tanks, a single rotor with two blades and short minor blades for inertial-stabilizing.
At least 2,407 of them have been built since its debut.
Type 5: Maritime Helicopters
A popular maritime helicopter is the Sikorsky MH-60R Sea Hawk, which was manufactured by Lockheed Martin and Sikorsky Aircraft Corporation. To meet the US Navy’s requirements, it can be operated in all weather and day or night. It replaced the SH-60Bs in the Navy’s helicopter inventory.
Measuring 55 feet in length, 15 feet in width, and 10 feet in height, it is a relatively large helicopter. It has a maz rotor diameter of 48 feet, and it weighs about 7,000 pounds when it is empty.
Its capacity is enough for 20,000 pounds of external stores, 1,3000 gallons of aviation fuel, and 245 extra gallons of emergency fluids. It can accommodate a crew of 4 and 4 passengers or 1,500 pounds of cargo.
The Seahawk can cruise at max speed of 162 knots and fly more than 160 knots. The minimum airspeed is 138 knots. When fully loaded, its ceiling is 13,1000 feet.
Impressively, without refueling, it can fly over 300 nautical miles. When necessary, its reserve fuel tank can extend the range to 460 nautical miles.
Type 6: Transport Helicopters
The Sikorsky CH-53E Super Stallion is the largest transport helicopter in the US military’s inventory. Its presence is undeniable in the forces. This giant heavy-lift helicopter debuted in 1981 and served diligently until 2004. It was based on the CH-53 Sea Stallion; the difference being a third engine and seventh blade.
The Sikorsky CH-53E Super Stallion can take off with a weight up to 73,500 pounds. It can lift more than 33 tons and transport up to 55 troops.
Apart from capacity, it Is impressive in other specs areas. Its cruising speed is 173 miles per hour and its range is 621 miles. On its own, the Sikorsky CH-53E Super Stallion weighs ~10,740 pounds and is nearly 28 feet high. It has:
It is also used by Chinese forces. A fun fact is that it is nicknamed the “Hurricane Make,” because it makes a downwash whenever it is operated.
Here is what the mighty helicopter looks like:
Type 7: Attack Helicopters
The Bell AH-1 SuperCobra is one of the most recognizable monsters in the US military attack helicopters’ inventory. It is manufactured by Bell Helicopter from the single-engine AH-1 Cobra. It is mostly used by the US Marine Corps, the Turkish Army, Iranian Army, and Chinese Army.
As an attack helicopter, the Bell AH-1 SuperCobra saw many conflicts. It was used by the Marine Corps in the Vietnam War, Invasion of Grenada’s Operation Urgent Fury, Gulf War, Somalia’s Operation Restore Hope, Operation Iraqi Freedom, and Afghanistan’s Operation Enduring Freedom, and 2003 Invasion of Iraq.
It can carry two crew members, and its fuel capacity is 460 gallons. Measuring 17.7 meters in length and 4.11 meters in height, this helicopter was considered an “ace” in the forces. It can takeoff and land with a max weight of 6,609 kilograms, and its max payload is 2,065 kilograms.
It can be armed with multiple armaments, such as the M197 3-barreled 20 mm Gatling cannons, 2.75 in. rockets, 5 in. Zuni rockets, and Sidewinder AIM-9 anti-aircraft missiles.
It was just recently retired (2020) replaced by the Bell Vipers.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have enjoyed reading about, “How many helicopters does the US military have & more.” You can bookmark our article for future reference. And for an even more complete understanding, we suggest looking into US Army aviation and Army planes and helicopters as well. But for now, leave us a comment! Any thoughts or questions are welcomed. We would love to hear from you.

I am Everett Bledsoe, taking on the responsibility of content producer for The Soldiers Project. My purpose in this project is to give honest reviews on the gear utilized and tested over time. Of course, you cannot go wrong when checking out our package of information and guide, too, as they come from reliable sources and years of experience.